 A next generation network is a packet-based network that can be used for both telephony and data and that supports mobility. Initially, the term Next Generation Network was used to refer to the transformation of the core network to IP. Sometimes an NGN is referred to as an all-IP network.
A next generation network is a packet-based network that can be used for both telephony and data and that supports mobility. Initially, the term Next Generation Network was used to refer to the transformation of the core network to IP. Sometimes an NGN is referred to as an all-IP network.
The ITU defined an NGN as:
“A Next Generation Network (NGN) is a packet-based network able to provide services including Telecommunication Services and able to make use of multiple broadband, QoS-enabled transport technologies and in which service-related functions are independent from underlying transport-related technologies. It offers unrestricted access by users to different service providers. It supports generalized mobility which will allow consistent and ubiquitous provision of services to users. ”
The NGN is characterized by the following fundamental aspects:
- Packet-based transfer
- Separation of control functions among bearer capabilities, call/session, and application/ service
- Decoupling of service provision from network, and provision of open interfaces
- Support for a wide range of services, applications and mechanisms based on service building blocks (including real time/ streaming/ non-real time services and multi-media)
- Broadband capabilities with end-to-end QoS and transparency
- Interworking with legacy networks via open interfaces
- Generalized mobility
- Unrestricted access by users to different service providers
- A variety of identification schemes which can be resolved to IP addresses for the purposes of routing in IP networks
- Unified service characteristics for the same service as perceived by the user
- Converged services between Fixed/Mobile
- Independence of service-related functions from underlying transport technologies
- Compliant with all Regulatory requirements, for example concerning emergency communications and security/privacy, etc.
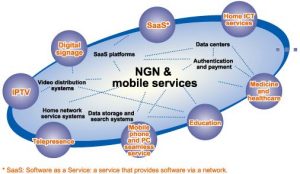
The Next-Generation Network (NGN) enables the deployment of access independent services over converged fixed and mobile networks – The NGN is packet based and uses IP to transport the various types of traffic (voice, video, data and signalling).
At the core of the harmonized ‘ALL IP’ NGN network is the IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) which provides an ‘access independent’ platform for a variety of access technologies (GSM, 3G, 4G, wi-fi, Cable, fibre and xDSL).
Standards for fixed NGN were developed by the now closed ETSI technical committee TISPAN. The TC has adopted the 3GPP™ core IMS specifications using Internet (SIP) protocols to allow features such as Presence, IPTV, Messaging, and Conferencing to be delivered irrespective of the network in use. Maintenance of NGN standards are now the responsibility of TC NTECH.

